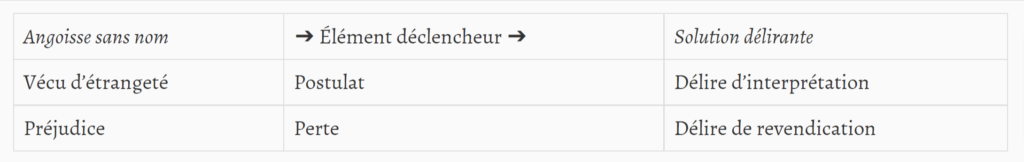
We speak, here, in terms of logical time, not chronological. In this relation, the interpretive delusion is often seen as a mode of recovery from chronic hallucinatory psychosis: by resorting to the postulate “Such and such an Other is persecuting me,” the subject becomes able to answer the question “What is happening to me?”. In the claim delusion, the occurrence of harm and the existence of an Object identified as the cause of the desire of an indeterminate Other (closer to “we” than to “he”) allow him not to remain uncertain about the intentions of the adverse instance. Through his delusion, the “claimant” implicitly completes the sentence that sums up the delusion of persecution, to state: “An Other (persecutes me because he) wants my Object”. This position makes it possible to contain the anguish induced by the desire of the Other (“What does he want from me?”) by reducing the question to a univocal answer: “It is not me that he wants, it is my Object that he wants”. The switch to the active register (“but I won’t let myself be done”) has the effect of overcoming the anxiety of retaliation.
If our hypotheses are correct, there are thus:
1. Identification of the persecution as the cause of the emergence of an experience of strangeness (“The Other persecutes me…”);
2. Designation of the Object as the cause of the desire of the Other (“… because they want my Object… “);
3. Struggle against the feeling of dispossession (“… but I will not let myself be dispossessed “).
Nous parlons, ici, en termes de temps logiques, et non chronologiques. Sous ce rapport, on considère souvent que le délire d’interprétation est un mode de guérison de la psychose hallucinatoire chronique : en recourant au postulat « Tel Autre me persécute », le sujet devient capable de répondre à la question « Que m’arrive-t-il ? ». Dans le délire de revendication, la survenue d’un préjudice et l’existence d’un Objet identifié comme cause du désir d’un Autre indéterminé (plus proche du « on » que du « il ») lui permettent de ne pas rester dans l’incertitude quant aux intentions de l’instance adverse. À travers son délire, le « revendicateur » complète implicitement la phrase qui résume le délire de persécution, pour énoncer : « Un Autre (me persécute parce qu’il) veut mon Objet » Cette position permet de contenir l’angoisse induite par le désir de l’Autre (« Que me veut-il ? ») en rabattant la question sur une réponse univoque : « Ce n’est pas à moi qu’il en veut, c’est mon Objet qu’on veut ». La bascule dans le registre actif (« mais je ne me laisserai pas faire ») a pour effet de surmonter l’angoisse de rétorsion.
Si nos hypothèses sont exactes, il y a donc :
1. Identification de la persécution comme cause de l’émergence d’un vécu d’étrangeté (« L’Autre me persécute… ») ;
2. Désignation de l’Objet comme cause du désir de l’Autre (« … parce qu’on veut mon Objet… ») ;
2. Lutte contre le sentiment de dépossession (« … mais je ne me laisserai pas faire »).
Benjamin Lévy, Alain Vanier, « Pour introduire une clinique de la revendication », Cliniques méditerranéennes, 2016/1 (n° 93), p. 161-174.
DOI : 10.3917/cm.093.0161.
URL : https://www.cairn.info/revue-cliniques-mediterraneennes-2016-1-page-161.htm